Article Is the Cloud More Secure? 4 Ways It's Safer Than You Think
According to the 2017 Insight Intelligent Technology Index, 41% of IT leaders view security as a primary concern when it comes to managing big data. Legacy systems can no longer provide the storage support needed to keep up with evolving workload demands — but the cloud can.
By Isabel Ticlo / 7 Apr 2018 / Topics: Cloud

Is cloud computing more secure? Here are four ways it keeps your data safe:
1. Built-in application security
Security remains the chief perceived barrier to cloud adoption, rated as the biggest obstacle by 53% (up from 45% the previous year) of survey respondents in the 2016 CloudPassage Cloud Security Spotlight Report.
But in most cases, the cloud is more secure than on-premise data centers because cloud providers have made — and continue to make — significant investments to ensure data protection. Many cloud services for business have security features built in, including application role-based authentication.
Although the infrastructure is secure, 53% of respondents to the CloudPassage survey see unauthorized employee access as the most significant threat to cloud security. But, by requiring users to verify credibility, your business can add a layer of protection against threats from unathurized access, hijacked accounts and malicious insiders. Cloud-based user authentication ultimately enables your company to access information anytime, anywhere while maintaining control and reducing risk.
2. A multifaceted approach
Some industries, such as healthcare and finance, may enforce stricter regulations when it comes to software or cloud use. A multilayered approach that meets compliance requirements can help mitigate cyberthreats before they develop into full-blown attacks. Employing both software-based and physical security solutions, cloud service providers tackle risk and data loss prevention in an integrated manner.
Uniting policy enforcement, management systems and encryption, cloud providers develop solutions that are compliant with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA), Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) and Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) standards.
3. Careful monitoring
With the ability to monitor resources, components and adherence to policies, cloud service providers can shut off any part of a system if something is affecting the overall security of the platform or service. Transparency and governance apply just as equally to the cloud as to the internal data center.
4. Stand-alone service
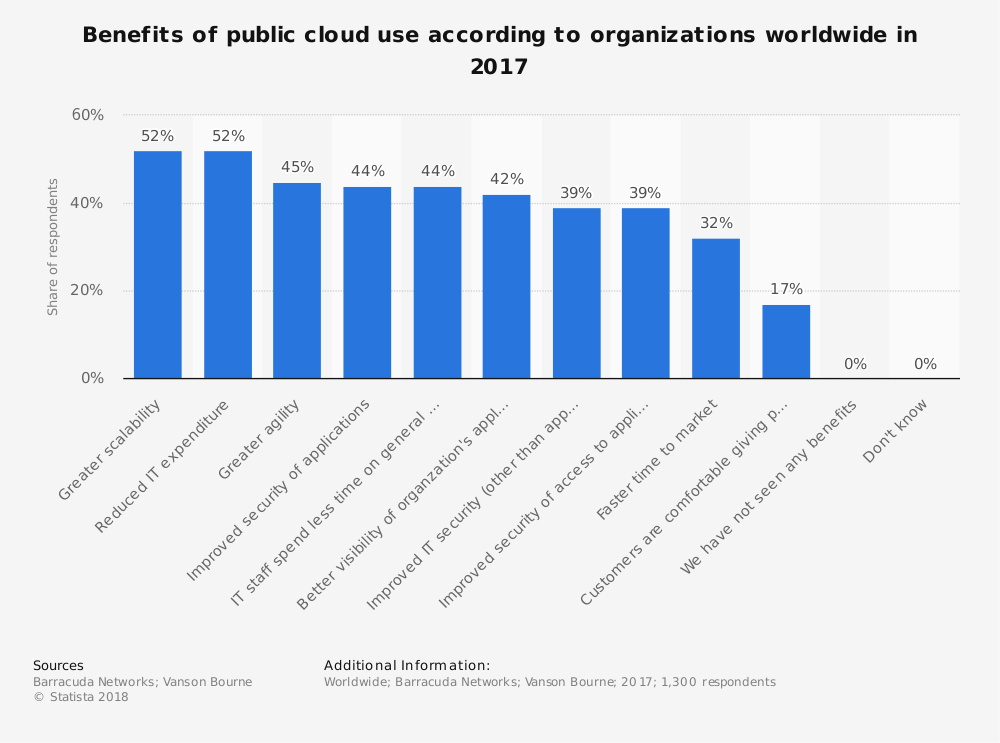
As shown in Figure 1, 44% of organizations worldwide believe improved security of applications is a top benefit of public cloud use. Other benefits include greater scalability, IT cost savings, greater agility and better use of time. The benefits of cloud computing are quickly outpacing the benefits of on-premise solutions. This has led to the evolution of the way security is delivered and employed by users.
To protect your company and its data while leveraging cloud computing services and tools, you may want to consider some additional solutions to help you along the way:
- McAfee hybrid cloud security solutions scale to meet business needs, keeping operational costs low.
- Symantec technology uses intelligence, simulations and monitoring to help analyze and prevent risks.
- Trend Micro endpoint security detects, prevents and responds to potential threats around data, the web and messaging.
The benefits of cloud computing create a real competitive advantage for your organization. The misconception about a lack of security shouldn’t stand in the way of increased productivity and flexibility.